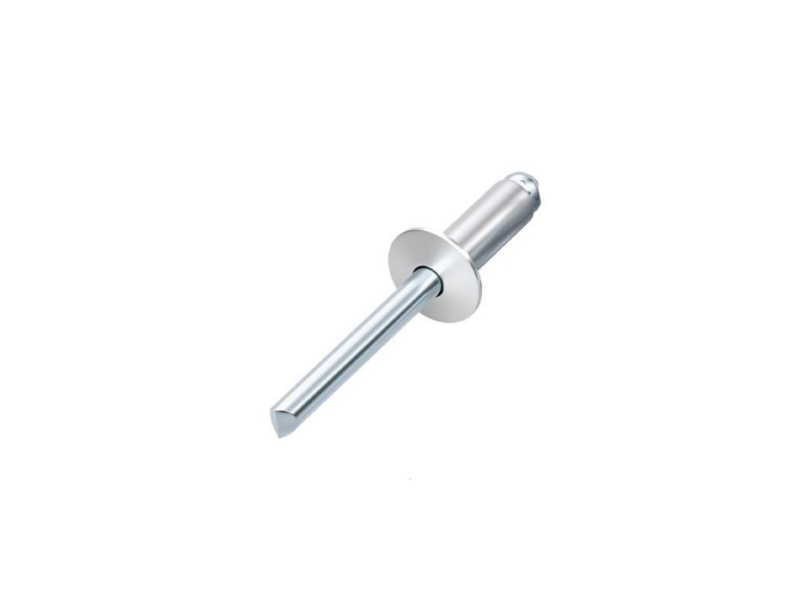
When you need a strong and lasting way to join materials, rivets are a reliable choice. This is especially true in high-vibration, heavy-load, or long-term situations. But what exactly are rivets used for? And when are they a better choice than screws or welding?
What Are Rivets?
A rivet is a kind of permanent fastener. It is used to join two or more materials. These materials are usually metal, plastic, or composite panels. Rivets do not use threads to hold things together. Unlike screws or bolts, once installed, a rivet forms a non-reversible connection.
A typical rivet consists of:
- A smooth cylindrical shaft (the rivet shank)
- A pre-formed rivet head
- A second head formed on the back side during installation, creating a secure lock
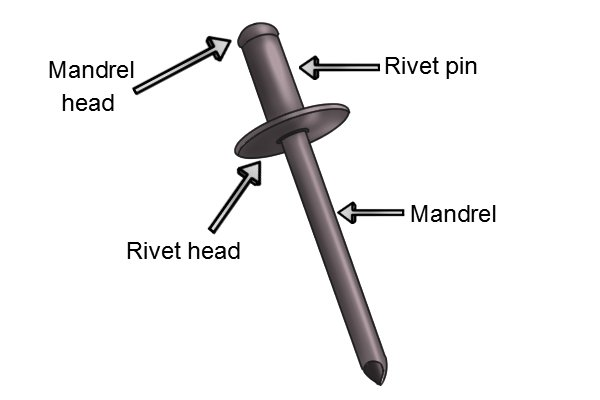
What Are Rivets Used For?
Rivets are ideal for applications that require:
- High-strength permanent fastening
- Excellent resistance to vibration
- Tamper-proof or tamper-resistant connections
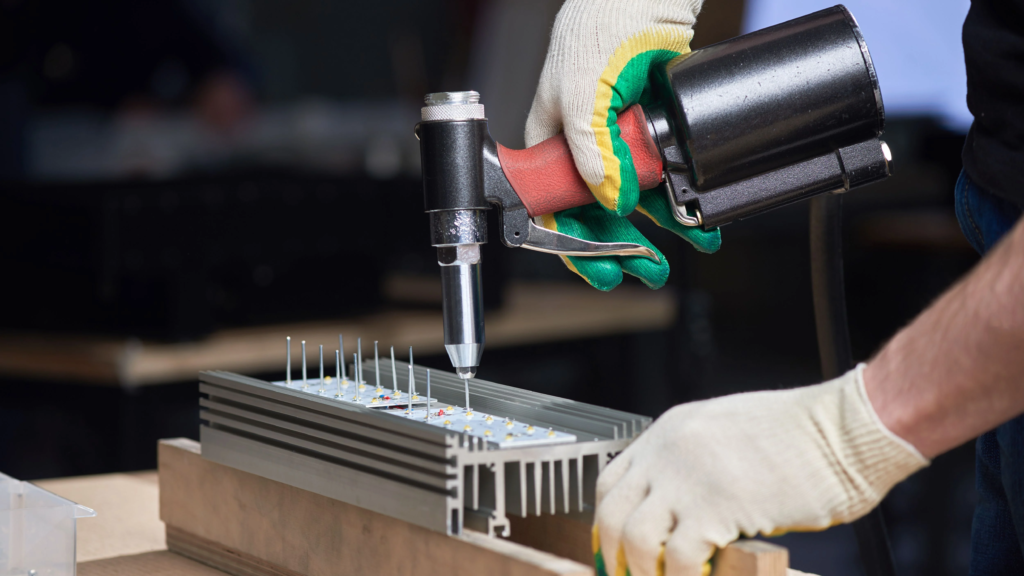

🔧 Common Use Cases by Industry:
| Industry | Typical Applications |
|---|---|
| Construction | Steel frameworks, metal panels, bridges |
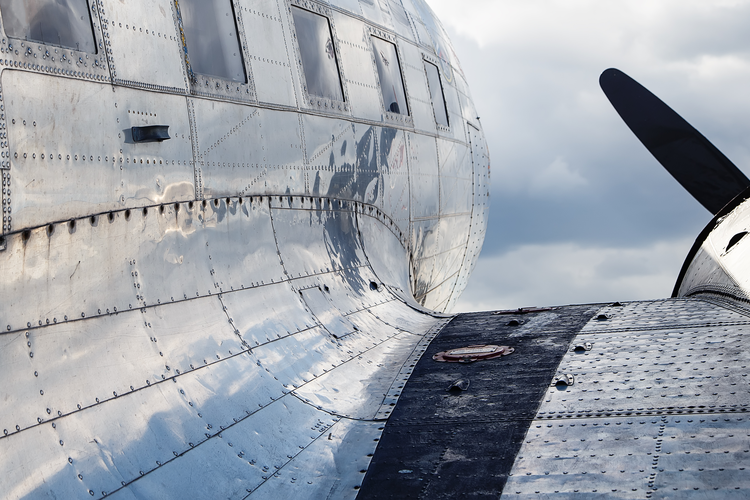
| Aerospace | Aircraft fuselages, wings, structural assemblies |
| Automotive | Car body panels, chassis components, interior trim |
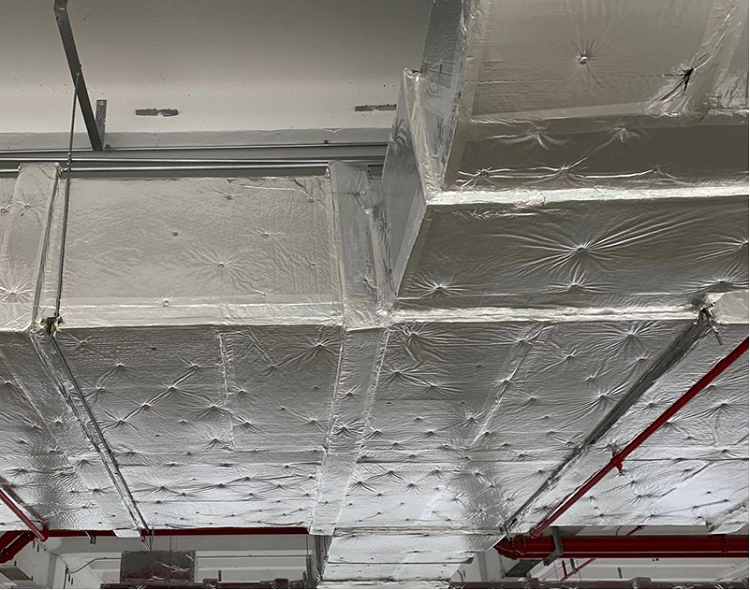
| Electrical & HVAC | Ductwork, enclosures, support brackets |
| DIY & Home Repair | Rain gutters, metal repair, furniture assembly |





Why Choose Rivets Instead of Screws or Welding?
| Feature | Rivets ✅ | Screws ❌ | Welding ✅ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Permanent connection | Yes | No | Yes |
| Tamper resistance | Yes | No | Yes |
| Vibration resistance | Excellent | Poor | Good |
| Easy installation | One-sided possible (blind rivets) | Easy | Requires equipment |
Rivets are especially useful when:
- You can only access one side of the material (use blind rivets)
- You need a clean and professional look
- Welding is not feasible or is too costly
Common Types of Rivets and Their Uses
| Type of Rivet | Recommended Applications |
|---|---|
| Blind Rivets (POP Rivets) | Single-side access, HVAC systems, DIY, thin metal |
| Solid Rivets | Aircraft structures, heavy-duty assemblies |
| Semi-tubular Rivets | Electronics, leatherwork, plastic parts |
| Drive Rivets | Metal-to-wood, architectural finishes |
| Structural Rivets | High-strength needs: steel frames, automotive frames |
How to Choose the Right Rivet
- Material Compatibility: Match rivet material to the materials being joined (e.g., aluminum rivet for aluminum sheet).
- Load Requirements: Use solid or structural rivets for heavy-duty loads.
- Accessibility: If you can only reach one side, choose blind rivets.
- Corrosion Resistance: For outdoor use, select stainless steel or aluminum rivets.
Rivet Installation Tips
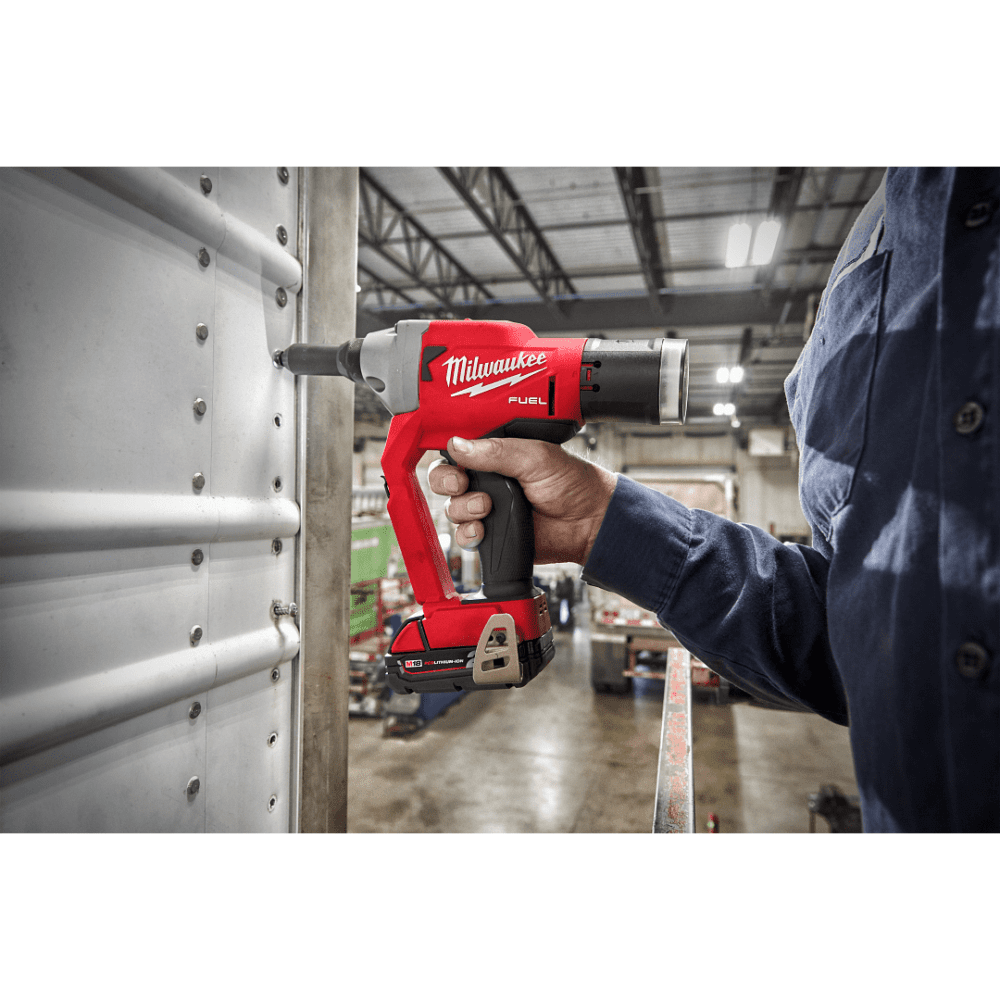
- Use the right rivet gun or rivet tool
- Choose the proper length and diameter based on material thickness
- Avoid under-setting or over-setting the rivet
- Always wear safety gloves and goggles
FAQ: What Are Rivets Used For?
Q1: Are rivets stronger than screws?
Yes. In high-stress or vibration-heavy environments, rivets offer a more durable and permanent bond than screws.
Q2: Can rivets be removed?
Rivets are designed for one-time installation. To remove them, you’ll typically need to drill them out.
Q3: What materials can rivets connect?
Rivets are commonly used for joining metal, plastic, wood, leather, and composite materials.
Q4: Where are blind rivets used?
Blind rivets are ideal for HVAC systems, automotive repairs, and applications with one-side access only.
Conclusion
If you’re searching for a secure, durable, and vibration-resistant fastening solution, rivets may be exactly what you need. From DIY projects to aerospace engineering, rivets continue to be an indispensable part of modern fastening technology.
So next time you ask yourself,
“What are rivets used for?”
Just remember: almost everything that needs to stay tight—uses rivets.




